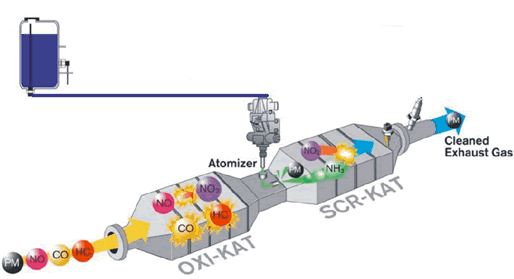
SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) - How it works
1. The AdBlue® tank is positioned alongside the regular diesel tank.
2. AdBlue® is injected in a finely atomised form into the exhaust gases. Exact metering ensures
the optimum mixture for every operating condition.
3. In the SCR catalyst, the toxic oxides of nitrogen are converted into nitrogen gas and water.
The catalytic converter is fully integrated into the exhaust silencer.
In comparison with diesel fuel, AdBlue® does not take up a lot of space. With approximately a 4% blend, 1000 litres of diesel fuel will only require around 40 litres of AdBlue®.
AdBlue® and the catalyst process �AdBlue® consists of an ammonia reagent – urea – and water. The heat in the exhaust system converts the urea into ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2). It is the ammonia that is the active substance and the main ingredient in the ongoing process in the SCR catalytic converter.
In the chemical-catalytic process that follows, the nitrogen oxides (NOx) are converted into nitrogen gas (N2) and water vapour (H2O). Nitrogen gas is a natural ingredient in the air we breathe. Any possible residues of ammonia are removed in the integrated Clean-Up catalytic converter.


|

